Gothic art was a Medieval art movement that lasted about 200 years. It began in France in Île-de-France at the Abbey Church of St Denis built by Abbot Suger, out of the Romanesque period in the mid-12th century, concurrent with Gothic architecture found in Cathedrals. By the late 14th century, it had evolved towards a more secular and natural style known as International Gothic, which continued until the late 15th century, where it evolved into Renaissance art. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Southern and Central Europe, never quite effacing more classical styles in Italy. In the late 14th century, the sophisticated court style of International Gothic developed, which continued to evolve until the late 15th century.
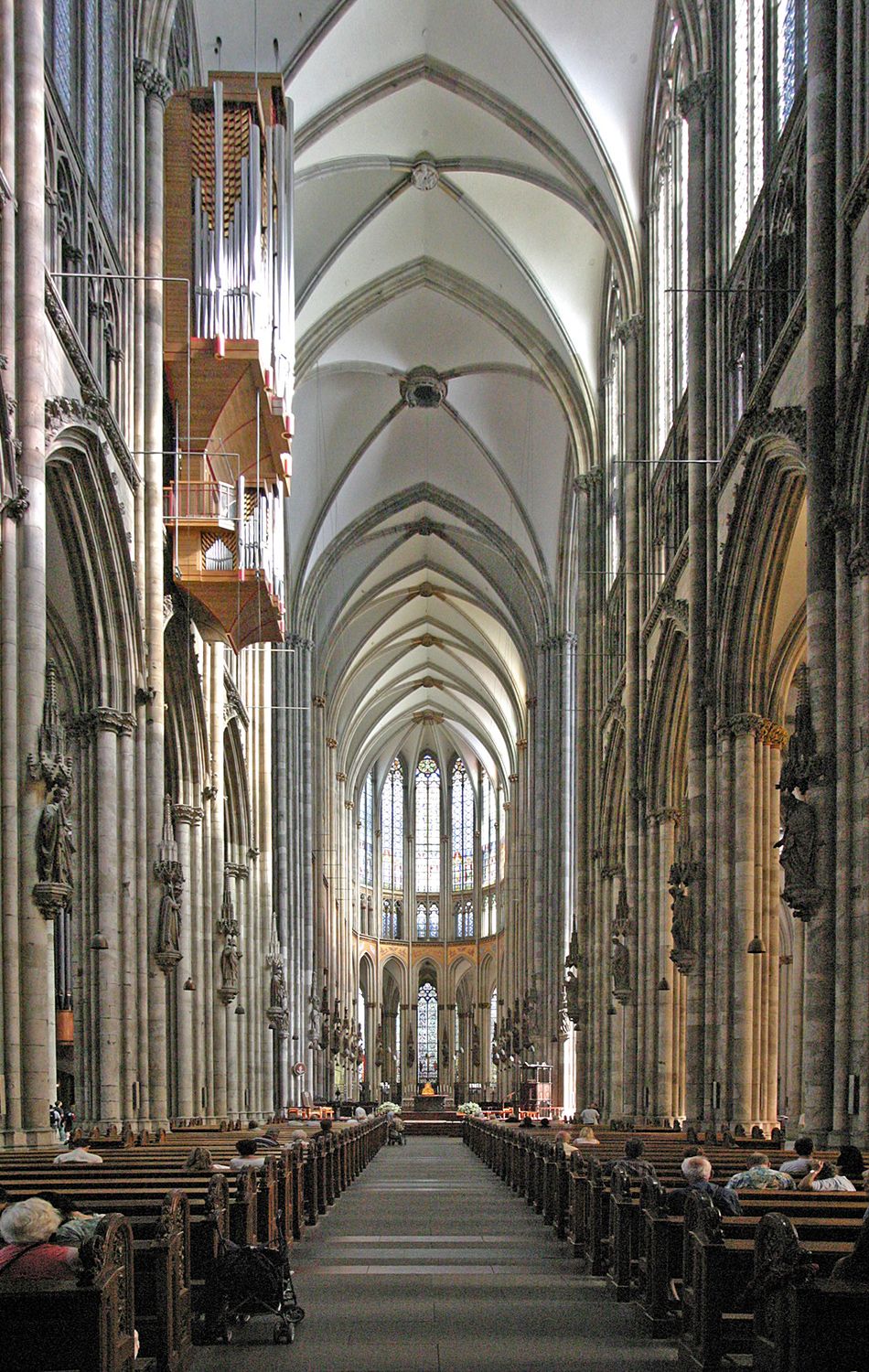
In many areas, especially Germany, Late Gothic art continued well into the 16th century, before being subsumed into Renaissance art. Primary media in the Gothic period included sculpture, panel painting, stained glass, fresco and illuminated manuscripts. The easily recognizable shifts in architecture from Romanesque to Gothic, and Gothic to Renaissance styles, are typically used to define the periods in art in all media, although in many ways figurative art developed at a different pace. Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. |
